Personal income tax avoidance methods disclosed by listed companies
Proper tax planning is absolutely allowed by tax law, but most tax planning is walking on the edge of tax evasion. Some unscrupulous practitioners are everywhere to deceive and promote malicious tax planning schemes. Such planning not only harms the adopters but also devalues the industry. In fact, there is not much room for planning in the field of personal income tax. The following so-called "tax avoidance" methods are real cases disclosed by listed companies or companies planning to go public in public documents such as prospectuses. Let's take a look.
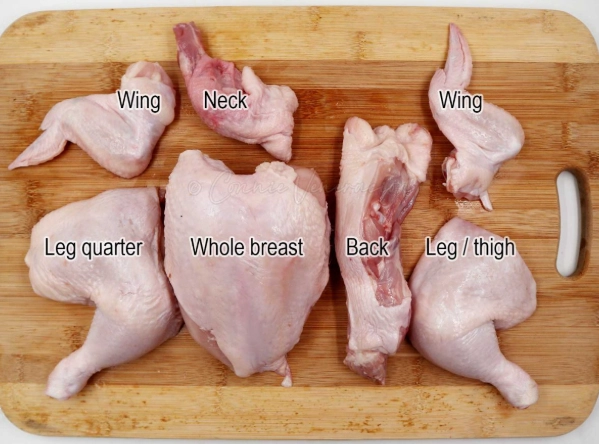
1. Off-site distribution of employee wages
Some companies will produce some waste materials in the production and operation process, and the sales targets of these waste materials are basically individuals, who do not need to issue invoices, so a part of the off-the-books income will be formed, which can be used to distribute year-end bonuses to executives and other employees. This is an ancient method of tax evasion.
2. Low-paid employees receive high salaries
Because personal income tax is a progressive tax rate, the highest tax rate is 45%, the higher the income, the heavier the tax burden, and its purpose is for the country to redistribute social wealth through taxation. Some taxpayers avoid the high tax rate by having low-paid employees receive part of the income of high-paid employees. This is not tax planning at all, but it can be called tax evasion planning.
3. Reimbursement of expenses to offset dividends
Individual shareholders need to pay 20% personal income tax on dividends, and many companies require shareholders to find invoices to offset dividends in order to pay less personal income tax for shareholders. So, air tickets, office supplies, computer consumables, etc., all come. It is said that a law firm that is not very large in scale listed more than 20 million air tickets in a year. But after the reform of the business tax, it is much more difficult to find invoices.
Tongyi Zhong: Due to the gift of the controlling shareholder and the reimbursement of medical expenses for employees without withholding personal income tax, it was fined 0.5 times the amount of personal income tax that should have been withheld but was not withheld, amounting to 162,200 yuan by the inspection bureau.
4. Step-by-step equity transferIn the regulations of personal income tax, when the income from equity transfer is significantly low but is considered to have a justifiable reason, the related parties include "spouses, parents, children, grandparents, maternal grandparents, grandchildren, maternal grandchildren, siblings, and those who have the direct obligation to support or maintain the transferor," such as foster parents or maintainers. If the equity is transferred to other individuals outside of the aforementioned related parties, such as a son-in-law, the equity transfer price must be fair. However, it is possible to achieve the goal through a step-by-step operation: first, transfer the equity at par value to the daughter, and then the daughter can transfer it at par value to her husband. Some say that through six people, one can know everyone in the country; then, through six steps of equity transfer, can it be transferred at par value to anyone?
V. Small and Micro Enterprises Issuing Invoices
Taxpayers establish small and micro enterprises and pay funds through fictitious procurement transactions with these enterprises. The small and micro enterprises issue invoices to the taxpayers, deduct relevant taxes, fees, and other expenses, and then withdraw cash to distribute salaries to some employees outside the books. These small and micro enterprises may either have a fixed tax collection or enjoy preferential policies on value-added tax and corporate income tax. Since the implementation of the inclusive tax reduction and fee reduction policy in 2019, such operations have become more prevalent. However, taxpayers face significant risks of tax evasion and the risk of small and micro enterprises issuing invoices fraudulently.
VI. Low-Priced Capital Increase Followed by Fixed Tax Collection
By undervaluing the target company through an inequitable capital increase, one can obtain a portion of the company's equity. Subsequently, by transferring the equity of the target company at market prices, the income obtained can be subject to fixed tax collection in areas where such collection is permissible, thus securing the profits.
VII. Who Loses in Targeted Dividend Distribution
Individuals need to pay personal income tax on dividend income, but legal entities that meet certain conditions can be exempt from corporate income tax. As a result, there has emerged a tax planning strategy known as "targeted dividend distribution," where individuals forgo dividends in favor of the company receiving them.
Targeted dividend distribution is not a normal business practice and usually occurs between related parties or through secret agreements. In the context of personal income tax avoidance through targeted dividend distribution, the relevant individuals gain tax benefits, but what is harmed is only the state's tax revenue, and it disrupts the tax order, causing great injustice to law-abiding operators.
The above are just a few of the "tax avoidance" techniques disclosed by some listed or prospective companies. In practice, there are various methods, truly a case of "each showing their own prowess," including traditional, modern, low-level, and high-level techniques such as splitting income, signing dual contracts, converting salary income to business income, and converting labor remuneration income to equity transfer income. Tax authorities will penalize taxpayers who engage in tax evasion under the guise of "reasonable tax avoidance" according to the tax collection and administration laws. Tax authorities often find it difficult to deal with taxpayers' tax avoidance behavior. Old Jiang calls on the relevant authorities to introduce measures as soon as possible, formulate anti-tax avoidance operations and management methods for personal income tax, and combat malicious tax avoidance behavior. In practice, some tax authorities have begun to try to challenge unreasonable business arrangements of enterprises using the "reasonable commercial purpose" clause. On August 20, 2021, a "Notice of Correction within a Time Limit" issued by a local tax bureau's tax office circulated online. This notice rarely cited the provisions of Article 8, Paragraph 3 of the Personal Income Tax Law, which states: If an individual obtains improper tax benefits through arrangements that do not have a reasonable commercial purpose, the tax authorities have the right to adjust the tax payment according to a reasonable method.



























Join the Conversation